MODULATION OF MITOCHONDRIAL MEDIATED APOPTOSIS BY SOLVENT FRACTIONS OF THE FRUIT EXTRACTS OF SARCOCEPHALUS LATIFOLIUS (SMITH) BRUCE
Keywords:
Apoptosis, cancer, MOMP, mPT pore, Sarcocephalus latifoliusAbstract
Aim and Objective: However, this claim has not been scientifically substantiated. In this study, we investigated the inductive effect of the crude methanol extract (CMESL) and a chloroform subfraction (sCFSL) of Sarcocephalus latifolius fruits on mPT, in vivo.
Methods: Thirty-five male wistar rats (90±10 g) were acclimatized, divided into seven groups, and treated with 1% DMSO (control) and 25, 50, and 100 mg/kgbw of each of the fractions for thirty days. Rats were sacrificed and liver mitochondria were isolated by differential centrifugation. The MOMP, DNA fragmentation, p53, Bax and BCl-2 protein expressions, Cytochrome C release, and caspase – 3 and -9 activities were assayed in liver tissue by standard methods.
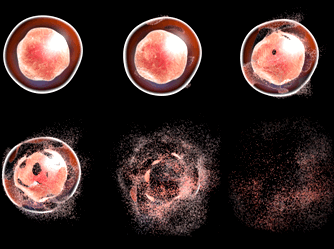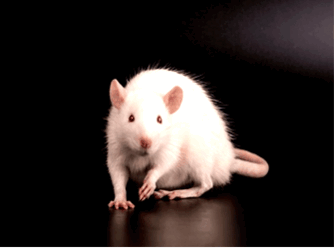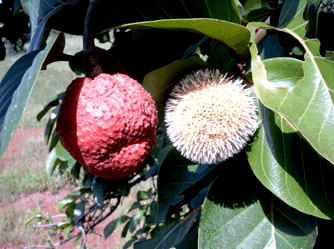
Results: CMESL and sCFSL induced mPT pore. The sCFSL induced MOMP maximally at 100 mg/kgbw, inhibited LPO (78%), enhanced mitochondrial ATPase activity (27.96±0.04 µmole/mg Protein/min) than CMESL (17.58± 0.03 µmole/mg Protein/min) at the same dose. Similarly, sCFSL caused DNA fragmentation; (77.33%), enhanced caspases -3 and -9 activation; increased p53 and Bax expression levels, increased Cytochrome C release, and downregulated BCl-2 protein expression, compared to CMESL.
Conclusion: These findings showed that sCFSL contains bioactive agents that can induce mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis, and therefore a potential target to be explored in the management of tumors and cancer.
Peer Review History:
Received 12 July 2024; Reviewed 19 September 2024; Accepted 24 October; Available online 15 November 2024
Academic Editor: Dr. Iman Muhammad Higazy , National Research Center, Egypt, imane.higazy@hotmail.com
, National Research Center, Egypt, imane.higazy@hotmail.com
Reviewers:
 Dr. Sangeetha Arullappan, Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman, Malaysia, sangeetha@utar.edu.my
Dr. Sangeetha Arullappan, Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman, Malaysia, sangeetha@utar.edu.my
 Dr. Nazim Hussain, North East Frontier Technical University, Arunachal pradesh, India, nhussain116@gmail.com
Dr. Nazim Hussain, North East Frontier Technical University, Arunachal pradesh, India, nhussain116@gmail.com
Downloads

Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









 .
.