COUMARIN ANALOGUES AS A POTENTIAL INHIBITOR OF LEISHMANIASIS: A MULTI-TARGETING PROTEIN INHIBITION APPROACH BY MOLECULAR DOCKING
Keywords:
Coumarins, leishmaniasis, molecular dockingAbstract
Objective: Leishmaniasis is one of the most dreadful diseases as a leading cause of death in most of the developed countries. Objective of the current work was to identify more potent and highly effective novel compound for the treatment of leishmaniasis.
Methods: In the given study molecular docking study was performed on the library of coumarin analogues as anti-leishmaniasis agents. Total 300 coumarins analogues were taken from Pubmed and were studied using a molecular docking study on trypanothione reductase from Leishmania infantum (PDB code: 2JK6 and 2P18) and Leishmania mexicana (PDB code: 3PP7).
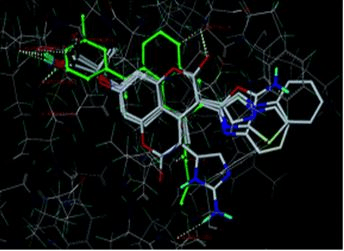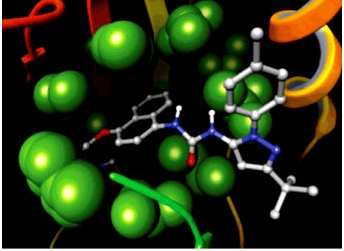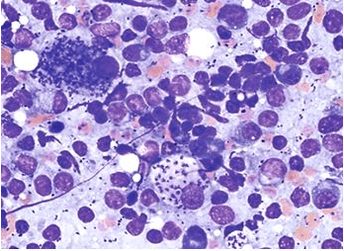
Results: Molecular docking result revealed that most active compound COU-130 and COU-220 bind to the active site of the protein with amino acids present in the various proteins. In PDB 2JK6 the active compound binds to the amino acid thr-51 and ser-14 were binding to the active site, and in PDB 3PP7 the active compound binds amino acid thr-26 and in PDB 2P18 the active compound binds to the amino acid phe-219 and try-212.
Conclusion: Further in vitro and in vivo study of selected coumarin analogues can be studied for their therapeutic potential in treating leishmaniasis.
Peer Review History:
Received 7 April 2019; Revised 9 May; Accepted 29 June; Available online 15 July 2019
Academic Editor: Dr. DANIYAN Oluwatoyin Michael , Obafemi Awolowo University, ILE-IFE, Nigeria, toyinpharm@gmail.com
, Obafemi Awolowo University, ILE-IFE, Nigeria, toyinpharm@gmail.com
Reviewer(s) detail:
Dr. Anthony C. C. Egbuonu , Michael Okpara University of Agriculture, Nigeria, tonycemalukegbuonu@yahoo.com
, Michael Okpara University of Agriculture, Nigeria, tonycemalukegbuonu@yahoo.com
Dr. Nicola Micale , University of Messina, Italy, nmicale@unime.it
, University of Messina, Italy, nmicale@unime.it
Downloads

Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









 .
.