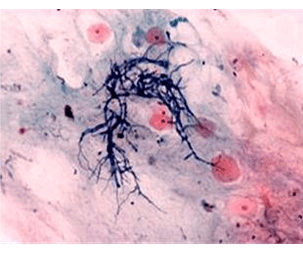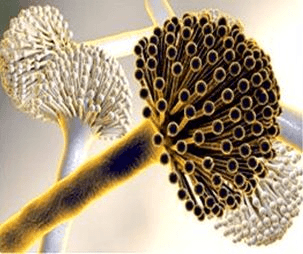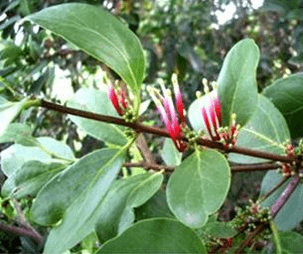
ANTIFUNGAL EFFECTS OF TAPINANTHUS GLOBIFERUS GROWING ON VITEX DONIANA AGAINST SOME FUNGAL ISOLATES
Keywords:
Antifungal, Phytochemical screening, Tapinanthus globiferusAbstract
Objective: Fungal infections are the major cause of many skin diseases, especially in developing countries. Natural products of medicinal value represent a potential source of chemotherapeutic agents. Tapinanthus globiferus has been used extensively in ethnomedicine for the treatment hypertension, ulcer, cancer, diabetes and fungal infections without a scientific basis. This work was aimed at screening the phytochemical constituents and evaluating the antifungal properties of methanol leaf extract its ethyl acetate and n-butanol fractions of T. globiferus against some clinical fungal isolates including Candida albicans, Trychophyton mentagrophytes, Trychophyton rubrum and Aspergillus niger using agar well diffusion and broth micro-dilution techniques.
Methods: Preliminary screening of phytochemical constituents of extract and fractions of T. globiferus indicated the presence of carbohydrates, alkaloids, glycosides, tannins, flavonoids, saponins, steroids and triterpenes.
Results: The methanol extract and its fractions demonstrated significant (P<0.05) antifungal effect against all the test organisms with mean zone of inhibition ranging from 27.83±0.16 – 14.46±0.29mm which was higher compared to that of the standard drug, Fluconazole (26.1±0.44 –18.49±0.16 mm). The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum fungicidal concentration (MFC) of the extract ranged between 6.25 – 25.0 mg/mL; ethyl acetate fraction had 3.13 – 25.0 mg/mL while n-butanol fraction had the least MIC ranging from 0.39-12.5 mg/mL against the test organisms.
Conclusion: Study concluded that T. globiferus have good antifungal activity validating the ethnomedicinal claim for the use of the plant in the treating fungal diseases.
Peer Review History:
Received 8 December 2019; Revised 14 January 2020; Accepted 28 February; Available online 15 March 2020
Academic Editor: Dr. Ali Abdullah Al-yahawi , Al-Razi university, Department of Pharmacy, Yemen, alyahawipharm@yahoo.com
, Al-Razi university, Department of Pharmacy, Yemen, alyahawipharm@yahoo.com
Reviewer(s) detail:
Dr. Gehan Fawzy Abdel Raoof Kandeel , Pharmacognosy Department, National Research Centre, Dokki, 12622, Giza, Egypt, gehankandeel9@yahoo.com
, Pharmacognosy Department, National Research Centre, Dokki, 12622, Giza, Egypt, gehankandeel9@yahoo.com
Prof. Dr. Ali Gamal Ahmed Al-kaf , Sana'a university, Yemen, alialkaf21@gmail.com
, Sana'a university, Yemen, alialkaf21@gmail.com
Dr. Mahmut Yıldıztekin , Muğla Sıtkı Koçman University, Turkey, mahmutyildiztekin@mu.edu.tr
, Muğla Sıtkı Koçman University, Turkey, mahmutyildiztekin@mu.edu.tr
Downloads

Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









 .
.