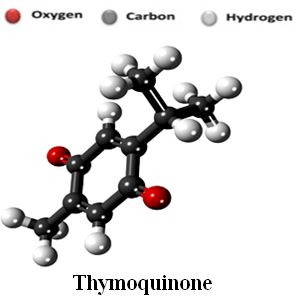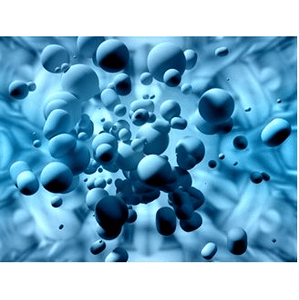
PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF THYMOQUINONE NANOPARTICLES PEGYLATED AS DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
Keywords:
Black Cumin, Nanoparticles, PEG 6000, Pegylation, ThymoquinoneAbstract
Objective: Thymoquinone is a main component of Black Cumin (Nigella sativa Linn.) with various pharmacological activities, but has poor stability and bioavailability. The purpose of this study was to carry out the preparation and characterization of timoquinone nanoparticles PEGylation.
Methods: The Thymoquinone nanoparticles (TQ-NP) were made with PEGylation using PEG 6000 with the concentrations on each preparation of 3 mM (A), 4 mM (B), and 5 mM (C) then were evaluated by the parameter of yield percentage Entrapment Efficiency (EE) and Drug Loading (DL), drug release, size and distribution particle, morphological analysis and Fourier Transform-Infrared spectrophotometer (FTIR).
Results: Thymoquinone nanoparticle was PEGylated with PEG 6000 has the highest efficiency entrapment of 99.9718±0.029% in formula A, with the capacity of drug loading 0,66%. Formulation A release 99.9718±0.029% of Thymoquinone at 50 minutes. The morphological observations with Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) showed spherical nanoparticles morphology.
Peer Review History:
Academic Editor: Dr. Nuray Arı , Ankara University, Turkiye, ari@ankara.edu.tr
, Ankara University, Turkiye, ari@ankara.edu.tr
Received 8 October 2020; Revised 11 November; Accepted 20 December; Available online 15 January 2021
Reviewer(s) detail:
Dr. Evren Alğin Yapar , Turkish Medicines and Medical Devices Agency, Turkiye, evren.yapar@yahoo.com
, Turkish Medicines and Medical Devices Agency, Turkiye, evren.yapar@yahoo.com
Dr. Sally A. El-Zahaby , Pharos University in Alexandria, Egypt, sally.elzahaby@yahoo.com
, Pharos University in Alexandria, Egypt, sally.elzahaby@yahoo.com
Downloads

Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









 .
.