ANALYSIS OF BIOFILMS FOR STREPTOCOCCUS MUTANS FROM DENTAL ROOT SURFACES OF ADULT PATIENTS WITH ROOT CARIES
Keywords:
Bacterial Load, root caries, Streptococcus mutansAbstract
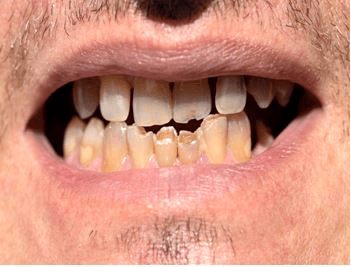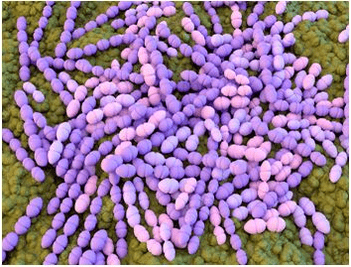
Background and objectives: Knowledge of the pathogenicity of the primary etiological factor of root caries, the microbial biofilm, might provide important information for the development of diagnosis and treatment strategies. This study assessed the numbers and revealed the proportion of Mutans streptococci , which is potential important cariogenic organisms, in biofilms collected from lesions at root surfaces with active caries lesions (ARC), inactive caries lesions, and sound root surfaces (SRS).
Material and methods: Samples were cultured in MSB agar for Mutans streptococci counts, and brain-heart infusion agar for total viable anaerobic counts. After incubation, the number of colony-forming units (CFUs) was determined and compared between groups by the Mann-Whitney U test with a significance level set at 95%. The proportion of counts of Mutans streptococci in the total viable microorganisms was also analyzed by Chi-square test. 108 samples (36 from each surface) from 36 patients were cultured and analyzed.
Results: The mean±SD for the counts of active root caries lesions was 7.47±9.89 10, significantly higher than that of inactive root caries lesions (2.5±0.97) and sound root surfaces (3.03±0.71). In conclusion, a trend towards higher counts was evident for ARC. In the ARC lesions among the dominant oral anaerobic bacteria, we could not identify streptococcal colonies (unspecified) in 11% while in IRC lesions it occurred in 47%, and SRS it occurred in 47%. In addition, in ARC the samples were ≥0.1-≥10 (CFU x10) ≥0.1-≥10 colonies of Streptococcus mutans.
Conclusion: In conclusion, a trend towards higher counts was evident for ARC and for most samples, the proportion of Streptococcus mutans was low relative to the viable number of total viable anaerobic microorganisms.
Peer Review History:
Received: 1 August 2021; Revised: 6 September; Accepted: 10 October; Available online: 15 November 2021
Academic Editor: Ahmad Najib , Universitas Muslim Indonesia, Indonesia, ahmad.najib@umi.ac.id
, Universitas Muslim Indonesia, Indonesia, ahmad.najib@umi.ac.id
Reviewers:
 Dr. Rawaa Souhil Al-Kayali, Aleppo University, Syria, rawah67@hotmail.com
Dr. Rawaa Souhil Al-Kayali, Aleppo University, Syria, rawah67@hotmail.com
 Dr. Tamer Elhabibi, Suez Canal University, Egypt, tamer_hassan@pharm.suez.edu.eg
Dr. Tamer Elhabibi, Suez Canal University, Egypt, tamer_hassan@pharm.suez.edu.eg
Downloads

Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









 .
.