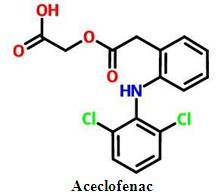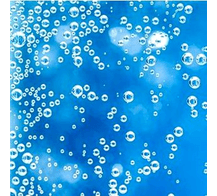
DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO DISSOLUTION STUDY OF BINARY AND TERNARY SOLID DISPERSIONS OF ACECLOFENAC
Keywords:
Aceclofenac, in-vitro dissolution, PEG 4000, PEG 6000, poloxamer, solid dispersionAbstract
Objective: The poor aqueous solubility of the drug exhibits in variable dissolution rate and hence poor bioavailability. Aceclofenac is poorly water soluble drug. The aim of the present study was to improve the water solubility and the dissolution rate of Aceclofenac by solid dispersion technique using different water soluble polymers. The term solid dispersions refer to the dispersions of one or more active ingredients in an inert carrier or matrix at solid state.
Methods: In this study, binary solid dispersion of Aceclofenac were prepared by fusion method using Polyethylene glycol 6000 (PEG 6000), Polyethylene glycol 4000 (PEG 4000), Poloxamer as carrier. Different drug-carrier weight ratio was used for this study. The effect of the carrier on the solubility and in-vitro dissolution were studied.
Results: It was found the drug was released 26.86% after 5 minutes and only 40.19% within 60 mins from active Aceclofenac on the other hand the release pattern of Aceclofenac from the binary solid dispersion formulations containing PEG 6000 in 1:5 ratio (Formulation coding: A5) showed the best result in comparison of other binary and ternary solid dispersion formulations which was 62.29% after 5 min and 83.03% within 60 mins. The hydrophilic polymers used for the preparation of solid dispersion are showed significant increase in the solubility of Aceclofenac.
Conclusion: This research showed that when Aceclofenac was dispersed in suitable water-soluble carriers such as PEG 6000, PEG 4000, Poloxamer, its dissolution were enhanced compared with pure drug.
Peer Review History:
Received 4 December 2018; Revised 13 January 2019; Accepted 1 March 2019; Available online 15 March 2019
Dr. Sally A. El-Zahaby , Pharos University in Alexandria, Egypt, sally.elzahaby@yahoo.com
, Pharos University in Alexandria, Egypt, sally.elzahaby@yahoo.com
Reviewer(s) detail:
Dr. Jennifer Audu-Peter , University of Jos, Nigeria, drambia44@gmail.com
, University of Jos, Nigeria, drambia44@gmail.com
Dr. Areen Alshweiat , University of Szeged, Hungary, areen.alshweiat@hu.edu.jo
, University of Szeged, Hungary, areen.alshweiat@hu.edu.jo
Downloads

Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









 .
.