DEVELOPMENT, CHARACTERIZATION, AND OPTIMIZATION OF REPAGLINIDE LOADED SPANLASTICS ALONG WITH INVESTIGATION OF DRUG SOLUBILITY IN VARIOUS MEDIA
Keywords:
Optimization, physicochemical characterization, repaglinide, solubility enhancement, spanlastics, thin-film hydration techniqueAbstract
Objective: This study seeks to explore the solubility of an antidiabetic drug with poor water solubility, Repaglinide (RPG), in various media, and develop and optimize RPG-loaded spanlastic formulations.
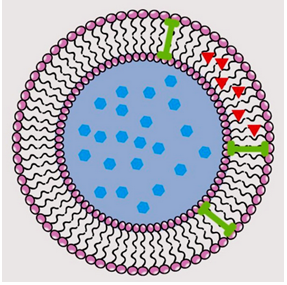
Methods: A 72-hours solubility study was conducted for RPG in different media, followed by UV spectrum analysis. Spanlastics containing RPG were prepared through the thin-film hydration (TFH) method combined with ultrasonication, incorporating varying concentrations ofthe lipophilic, non-ionic surfactant agents, Span 60 and Tween 80. Characterization was performed To assess particle size (PS), polydispersity index (PDI), zeta potential (ZP), and entrapment efficiency (EE%). Optimization was achieved by analysing characterization results and using a mixture design of Design Expert software which predicted the optimized formula.
Results: RPG exhibited the highest solubility in phosphate buffer saline (PBS, pH 6.8) incorporating 0.5% Tween 20 (168.595 µg/mL), followed by PBS with 0.1% Tween 80 (80.355 µg/mL), PBS alone (56.163 µg/mL), and PBS with 0.1% sodium lauryl sulphate (SLS) (53.706 µg/mL). UV scanning in methanol revealed three characteristic absorption bands for RPG, with peak selection optimized for molar absorptivity in each medium. The RPG-loaded spanlastic formulations demonstrated nano-sized vesicles with uniform size distribution, high stability, and efficient drug encapsulation. Optimized spanlastics predicted a particle size 126.162 nm, PDI 0.416, ZP-43.258 mV, and EE% 77.753%.
Conclusions: This research emphasizes the potential of optimized RPG-loaded spanlastics, developed through the thin-film hydration method, as a promising approach for improving the solubility and stability of poorly water-soluble drugs. RPG showed the highest solubility in PBS (pH 6.8) containing 0.5% Tween 20, and the formulation achieved desirable nanosize, uniformity, and high encapsulation efficiency.
Peer Review History:
Received 12 July 2024; Reviewed 16 September 2024; Accepted 23 October; Available online 15 November 2024
Academic Editor: Dr. Asia Selman Abdullah , Pharmacy institute, University of Basrah, Iraq, asia_abdullah65@yahoo.com
, Pharmacy institute, University of Basrah, Iraq, asia_abdullah65@yahoo.com
Reviewers:
 Antonio José de Jesus Evangelista, Federal University of Ceará, UFC, Brazil, tony_biomed@hotmail.com
Antonio José de Jesus Evangelista, Federal University of Ceará, UFC, Brazil, tony_biomed@hotmail.com
 Asmaa Ahmed Mohamed Ahmed Khalifa, Pharos University, Alexandria, Egypt, asmaa.khalifa@pua.edu.eg
Asmaa Ahmed Mohamed Ahmed Khalifa, Pharos University, Alexandria, Egypt, asmaa.khalifa@pua.edu.eg
Downloads

Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









 .
.