COMPARATIVE OUTCOMES IN MANDIBULAR ANGLE FRACTURE MANAGEMENT RECONSTRUCTION PLATES VERSUS DUAL MINIPLATES FIXATION
Keywords:
Complication rate, double miniplate fixation, mandibular angle fractures, reconstruction platesAbstract
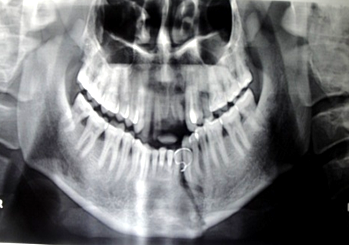
Background and aims: The angle created by the positioning of the ramus and mandibular body is known as the mandibular angle. An angle fracture is characterized by a triangular region that is enclosed by the masseter muscle's anterior border and an oblique line that runs from the mandibular third molar region to the masseter muscle's posterior inferior attachment. This study examined the results and side effects of utilizing reconstruction plates against double miniplate fixation for treating mandibular angle fractures.
Materials and methods: The Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery at the Al-Thorah Hospital in Sana'a, Yemen, carried out the study between 2020 and 2024, diagnosing mandibular angle fractures in two equal groups. Reconstruction plates were used for 20 patients in Group A, and double miniplate fixation was used for another 20 patients in Group B. Following surgery, the two groups had radiographic and clinical evaluations for mandibular deviation, hematoma, infection, limited mouth opening, surgical site edema, plate exposure, plate stability, and malocclusion.
Results: The study found that 15% of patients treated with reconstruction plates experienced bone exposure, 10% experienced impaired stability, 30% reported plate-site edema, and 15% reported nerve injury, compared to the 10% treated with two miniplates. The study found that the use of two miniplates was better at reducing deviation opening in patients treated with two miniplates, with a difference of 15% and a p-value of 0.07.
Conclusion: The study found that fixation using two miniplates is the most effective and reliable treatment strategy for mandibular angle fractures, with lower complication rates and minimal infection rates. Further studies are needed to determine the optimal approach for fixing these fractures.
Peer Review History:
Received 7 April 2025; Reviewed 10 May 2025; Accepted 21 June; Available online 15 July 2025
Academic Editor: Dr. Amany Mohamed Alboghdadly , Ibn Sina National College for Medical Studies in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, amanyalboghdadly@gmail.com
, Ibn Sina National College for Medical Studies in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, amanyalboghdadly@gmail.com
Reviewers:
 Dr. A.A. Mgbahurike, University of Port Harcourt, Nigeria, amaka_mgbahurike@yahoo.com
Dr. A.A. Mgbahurike, University of Port Harcourt, Nigeria, amaka_mgbahurike@yahoo.com
 Dr. Adebayo Gege Grace Iyabo, University of Ibadan, Nigeria, funbimbola@gmail.com
Dr. Adebayo Gege Grace Iyabo, University of Ibadan, Nigeria, funbimbola@gmail.com
Downloads

Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Universal Journal of Pharmaceutical Research

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









 .
.