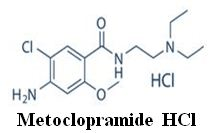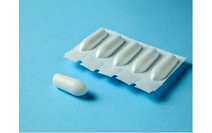
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF METOCLOPRAMIDE HCL RECTAL SUPPOSITORIES
Keywords:
Hydrogenated vegetable oil, in-vitro release study, Metoclopramide hydrochloride, suppositoriesAbstract
Objective: Metoclopramide hydrochloride is a dopamine receptor antagonist, used mostly for stomach and esophageal problems as it is a prokinetic agent. The aim of the present study was to design and evaluate the suppositories of Metoclopramide HCl.
Methods: Six different, rectal suppositories were developed by fusion (pour-moulding) method by employing various hydrophilic and hydrophobic polymeric bases like gelatin, PEG-400 and hydrogenated vegetable oil using propylene glycol as plasticizer and beeswax as hardening agent. Metoclopramide HCl suppositories were evaluated for appearance, weight variation, drug content uniformity, liquefaction time and temperature, micro-melting range, disintegration and in-vitro release study. The in-vitro release rate data was evaluated statistically and was found that from all the formulations the drug release is by diffusion mechanism.
Results: Optimum formulation of batch S1 has shown 83.427% Metoclopramide HCl in a study of 2 hrs. These drug release results are supported by the disintegration time of suppositories. Lesser the disintegration time faster the drug release. All formulations has shown zero, first and Higuchi release kinetics.
Conclusion: The result suggests that the Metoclopramide HCl suppositories can be prepared by employing hydrophilic and hydrophobic polymers.
Peer Review History:
Received 25 October 2018; Revised 4 November; Accepted 25 December; Available online 15 January 2019
Academic Editor: Dr. Nuray Arı , Ankara University, Turkiye, ari@ankara.edu.tr
, Ankara University, Turkiye, ari@ankara.edu.tr
Reviewer(s) detail:
Dr. Mahmoud S. Abdallah , University of Sadat city, Egypt, dr_samy777@yahoo.com
, University of Sadat city, Egypt, dr_samy777@yahoo.com
Dr. Sunita Singh , Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, USA, sunita.nccs@gmail.com
, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, USA, sunita.nccs@gmail.com
Downloads

Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









 .
.