A COMPREHENSIVE REVIEW ON SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS: A PROMISING DOSAGE FORM
Keywords:
Controlled release, extended release, in-vitro dissolution, matrix tablet, polymersAbstract
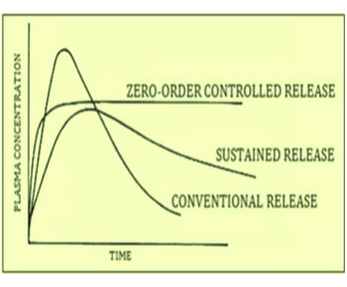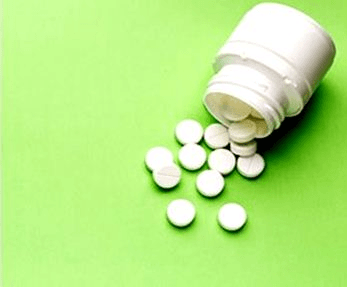
Oral ingestion is most convenient and commonly employed route of drug delivery due to its ease of administration, least aseptic and flexibility in the design of dosage form. The objective of the study was to explore the necessity, advantages and various techniques of extended release matrix tablet to get a constant drug delivery rate and reproducible kinetics for advance delivery. Different types of extended release matrix tablet have been explained briefly along with the various formulation which mainly by wet granulation or direct compression method or by dispersion of solid particle within a porous matrix formed by using different polymers. Matrix controls the free rate of drug. Matrix tablets can be formulated by either direct compression or wet granulation method by using a variety of hydrophilic or hydrophobic polymers. The extended release matrix tablets can assure better patient compliance through reduction in total dose and dosage regimen, which can be great help to treat chronic diseases. This review highlights the types of matrices, mechanisms involved and evaluation studies.
Peer Review History:
Received 22 September 2018; Revised 2 November; Accepted 26 December; Available online 15 January 2019
Academic Editor:
Dr. Iman Muhammad Higazy , National Research Center, Egypt, imane.higazy@hotmail.com
, National Research Center, Egypt, imane.higazy@hotmail.com
Reviewer(s) detail:
Dr. Sally A. El-Zahaby , Pharos University in Alexandria, Egypt, sally.elzahaby@yahoo.com
, Pharos University in Alexandria, Egypt, sally.elzahaby@yahoo.com
Dr. Maha Khalifa Ahmed Khalifa , Al-Azhar Universit - Cairo, Egypt, mahakhalifa.ahmed@hotmail.com
, Al-Azhar Universit - Cairo, Egypt, mahakhalifa.ahmed@hotmail.com
Downloads

Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









 .
.