CLINICAL EFFECTS OF PLATELETS RICH FIBRIN (PRF) FOLLOWING SURGICAL EXTRACTION OF IMPACTED LOWER THIRD MOLARS AMONG A SAMPLE OF YEMENI ADULTS
Keywords:
Edema, impacted third molar surgery, pain, Platelet rich fibrin (PRF), trismusAbstract
Background and aims: Third molar surgery is one of the most frequent procedures in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Pain, trismus, and swelling are the majority symptoms that have an impact on patients' quality of life. Haemorrhage, alveolitis and infections are general complications. Several endeavors have been through to decrease the possibility of complications and make better patients' quality of life, such as the administration of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) or the administration of platelet-rich fibrin (PRF). The aim of this study is to determine the clinical consequences of PRF subsequent to surgical extraction of impacted lower third molars among a sample of Yemeni adults by evaluate the PRF effect on postoperative complications of pain, swelling, and mouth opening and to compare the difference in the healing process between the PRF surgery site and the control site.
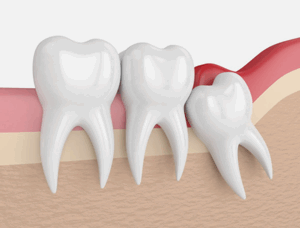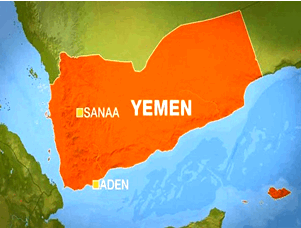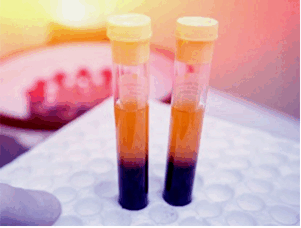
Methods: The prospective study consisted of 36 patients who obtainable for subtraction of an impacted bilateral mandibular molar. Subsequent to extraction, plugs were filled up with PRF or without PRF in the study (18 patients) and comparative control (18 patients) groups, respectively. Postoperative edema was calculated using a flexible tape measure by estimating the distance between several facial features on the 2nd to the 7th postoperative days. Postoperative pain was assessed using a line-type visual analog scale (VAS) and a verbal scale (VRS); and trismus by caliper scales. Epi-Info version 7.0 was used for data analysis.
Results: There were statistical significant variations concerning the PRF group and the control group in regard to pain intensity, number of analgesics tablets used and the interincisal distance, as the p value were 0.001, 0.0001 and 0.001 respectively.
Conclusion: The PRF helps in reducing the post-surgical pain, edema and trismus. As well as accelerate healing process after the application to the socket of surgically extracted lower third molar.
Peer Review History:
Received: 8 October 2022; Revised: 10 November; Accepted: 22 December 2022, Available online: 15 January 2023
Academic Editor: Prof. Dr. Gorkem Dulger , Duzce University, Turkey, gorkemdulger@yandex.com
, Duzce University, Turkey, gorkemdulger@yandex.com
Reviewers:
 Dr. George Zhu, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran, sansan4240732@163.com
Dr. George Zhu, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran, sansan4240732@163.com
 Dr. Tamer Elhabibi, Suez Canal University, Egypt, tamer_hassan@pharm.suez.edu.eg
Dr. Tamer Elhabibi, Suez Canal University, Egypt, tamer_hassan@pharm.suez.edu.eg
Downloads

Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









 .
.