CONFORMATIONAL STUDY OF MOLECULES IN A BIOLOGICAL ENVIRONMENT, DESIGN OF INHIBITORS OF HUMAN AMINOPEPTIDASE M1 IMPLICATED IN CANCER THERAPY
Keywords:
ADMET, complexation model, Drug design, molecular modeling, pharmacophore model, QSAR modelAbstract
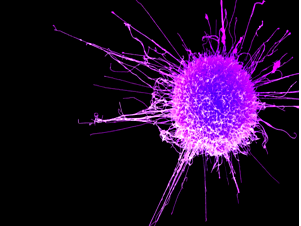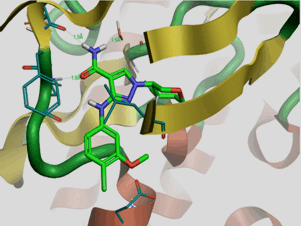
Objective: A novel subnanomolar anticancer hydroxamic acid containing drug candidates, inhibitors of human M1 aminopeptidase (APN) a recent validated target and has reached the predicted subnanomolar range of inhibitory potency.
Methods: A quantitative structure activity relationships (QSAR) complexation model has been developed from a compounds of 37 hydroxamic acid derivatives (AHD1-37 as training set, TS) to establish a linear correlation between the calculated relative Gibbs free energies (GFE: ΔΔGcom) of APN-AHDx complex formation and the experimental inhibition potency (Kiexp). The predictive power of the QSAR model was then validated first with 9 other AHDs not included in the TS and thereafter with the generation of a 3D-QSAR-PH4 pharmacophore (PH4) model to screen the AHD chemical subspace built as a virtual combinatorial library of more than 58,644 AHD analogs). Finally the best PH4 hits were evaluated with the initial QSAR model for predicted potency (Kipre) and pharmacokinetic profile.
Results: The QSAR model linear correlation equation: pKiexp=-0.1901×∆∆Gcom + 8.2886 , R2=0.94, the subsequent PH4 model linear correlation between experiment and PH4-estimated Ki: pKiexp=1.0006× pKipre + 0.0028, R2=0.79 documents the high predictive power of this approach. Finally the screening of the virtual library of AHD analogs yielded 95 orally bioavailable candidates the best reaching a predicted potency (Kipre) of 50 pM and displaying favorable pharmacokinetic profile.
Conclusion: The combined use of molecular modeling (QSAR) and in silico PH4-based screening of the hypothetical combinatorial library has resulted in proposed and predicted potent anticancer candidates with a suitable pharmacokinetic profile.
Peer Review History:
Received: 8 August 2023; Revised: 3 September; Accepted: 29 October; Available online: 15 November 2023
Academic Editor: Dr. Nuray Arı , Ankara University, Turkiye, ari@ankara.edu.tr
, Ankara University, Turkiye, ari@ankara.edu.tr
Reviewers:
 Prof. Hassan A.H. Al-Shamahy, Sana'a University, Yemen, shmahe@yemen.net.ye
Prof. Hassan A.H. Al-Shamahy, Sana'a University, Yemen, shmahe@yemen.net.ye
 Prof. Dr. A. Hakan AKTAŞ, Süleyman Demirel University, Faculty of Science and Art, Department of Chemistry, Isparta-Turkey, hakanaktas@sdu.edu.tr
Prof. Dr. A. Hakan AKTAŞ, Süleyman Demirel University, Faculty of Science and Art, Department of Chemistry, Isparta-Turkey, hakanaktas@sdu.edu.tr
Downloads

Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









 .
.