MAXILLOFACIAL FRACTURE TYPE AND THEIR MANAGEMENT IN INDIVIDUALS REFERRED TO THE MILITARY HOSPITAL IN SANA’A CITY, YEMEN
Keywords:
Facial fractures, mandibular fracture, maxillary fracture, maxillofacial injuries, open surgical fixation, zygomatic fractureAbstract
Background and aims: Maxillofacial fractures, injuries to facial bones, are treated based on type and severity, including common types like mandible, maxilla, zygomatic bone, and nose. University hospitals like Military Hospital use advanced surgical techniques and multidisciplinary care to handle complex cases requiring closed reduction or open reduction and internal fixation. This retrospective study aimed to examine the types and treatment of maxillofacial fractures among individuals referred to the Military Hospital in Sana'a, assess associated complications, evaluate recovery experience, and postoperative quality of life.
Materials & methods: The records of 94 patients, ages 8 to 60, who suffered maxillofacial fractures between January 1, 2022, and December 29, 2022, were examined in this retrospective analysis. From the archival records, information about age, gender, the location and cause of the fracture, and the method of treatment was extracted and examined.
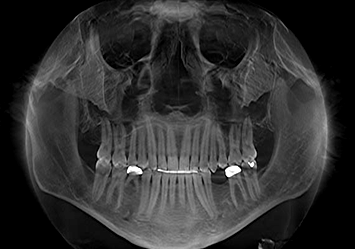
Results: The study involved 94 patients aged 8-60, mostly 16-25, with traffic accidents being the most common cause. Fractures were common, with symphysis being the most common type (62.8%), followed by zygomatic (30.9%). Other types included palate, lateral, suspensory, maxillary sinus, and alveolar process fractures. The study revealed that nasal bridge fractures were the most common nasal bone fracture, accounting for 7.4% of cases. Orbital and facial fractures accounted for 12.8% and 5.3%, respectively.
Conclusions: Traffic accidents were the most common cause of fractures, and the most common type of fracture was a symphysis fracture, followed by a zygomatic fracture. Other types included fractures of the palate, lateral, suspensory, maxillary sinus, and alveolar process.
Peer Review History:
Received 2 June 2025; Reviewed 11 July 2025; Accepted 17 August; Available online 15 September 2025
Academic Editor: Prof. Dr. Gorkem Dulger , Duzce University, Turkey, gorkemdulger@yandex.com
, Duzce University, Turkey, gorkemdulger@yandex.com
Reviewers:
 Dr. Andrzej Szymański, Poznan University of Technology, Poland, andrzej.szymanski@put.poznan.pl
Dr. Andrzej Szymański, Poznan University of Technology, Poland, andrzej.szymanski@put.poznan.pl
 Dr. Anthony C. C. Egbuonu, Michael Okpara University of Agriculture, Nigeria, tonycemalukegbuonu@yahoo.com
Dr. Anthony C. C. Egbuonu, Michael Okpara University of Agriculture, Nigeria, tonycemalukegbuonu@yahoo.com
Downloads

Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Universal Journal of Pharmaceutical Research

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









 .
.