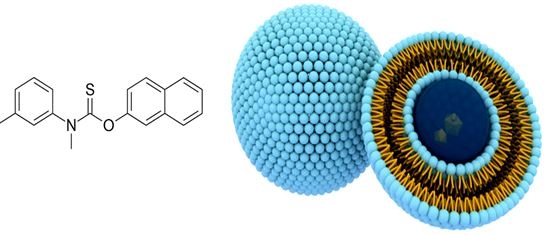
TOLNAFTATE LOADED LIPOSOMES- DESIGN, AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION
Keywords:
Tolnaftate, liposomes, phospholipid, entrapment efficiency, zeta potential, in-vitro drug releaseAbstract
Objectives: Liposomes are colloidal particles formed as concentric bimolecular layers that are capable of encapsulating drugs. Liposomes have the potential for extending the duration of action for days or months. Tolnaftate is used as the topical antifungal agent. The purpose of this study was to provide the delivery of the topical drug at a sustained rate across intact skin to improve bioavailability.
Methods: In present study, four different liposomes formulations of Tolnaftate were prepared by ethanol (solvent) injection method by varying the concentrations of phospholipids. The prepared liposomes were characterized for size, shape, entrapment efficiency, zeta potential, in-vitro drug release.
Results: The % entrapment efficiency was found to be in the range of 90.24, 90.75, and 90.75%. The % entrapment efficiency of optimized batch LS4 was found to be 90.74 %. An in vitro drug release of about 82.114 % in 10 h was observed from optimum formulation of batch LS4.
Conclusion: Based on different parameters like particle size, entrapment efficiency, drug release formulations of batch LS4 was selected as best formulation. Study concludes that Tolnaftate liposomes have potential for providing sustained delivery of drug.
Peer Review History:
Article received on- 23 September 2016; Revised on- 6 November; Accepted on- 9 December; Available online 15 January 2017
Academic Editor: Dr. Amany Mohamed Alboghdadly , Princess Nourah bint abdulrahman university, Riyadh, amalbgadley@pnu.edu.sa
, Princess Nourah bint abdulrahman university, Riyadh, amalbgadley@pnu.edu.sa
Reviewer(s) detail:
Dr. Mahmut Yıldıztekin , Muğla Sıtkı Koçman University, Turkey, mahmutyildiztekin@mu.edu.tr
, Muğla Sıtkı Koçman University, Turkey, mahmutyildiztekin@mu.edu.tr
Dr. Mohamed Derbali , Faculty of Pharmacy, Monastir, Tunisia, mohamed.edderbali@gmail.com
, Faculty of Pharmacy, Monastir, Tunisia, mohamed.edderbali@gmail.com
Downloads

Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









 .
.